Platform
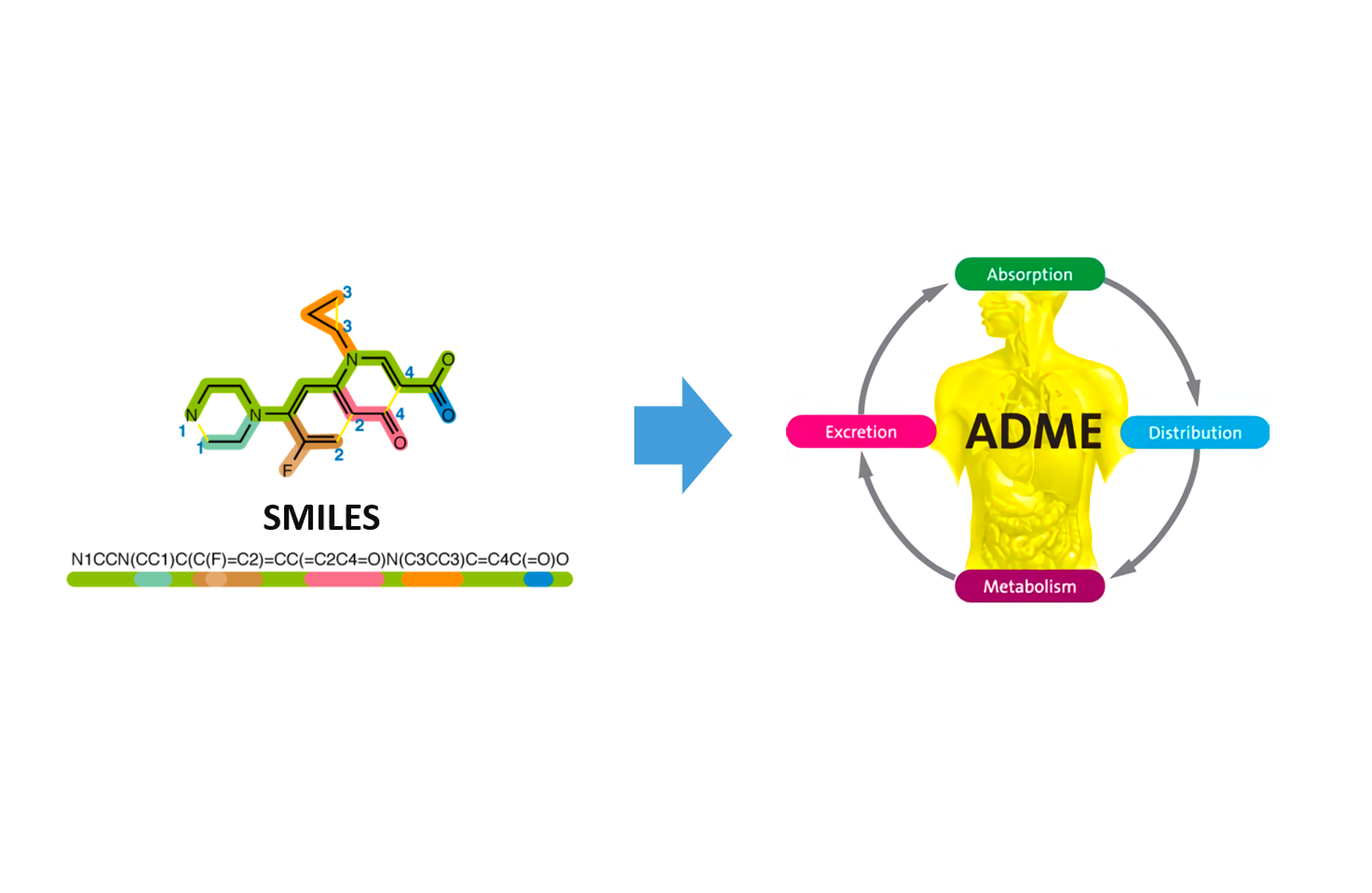
LiLac-ADMET
Figuring compound's properties of absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity so called ADMET features is one of the important steps for clinical stages of drug development. Successful prediction of certain properties of ADMET prevents unnecessary costs of development and help boosting up the process by helping critical decision-making.
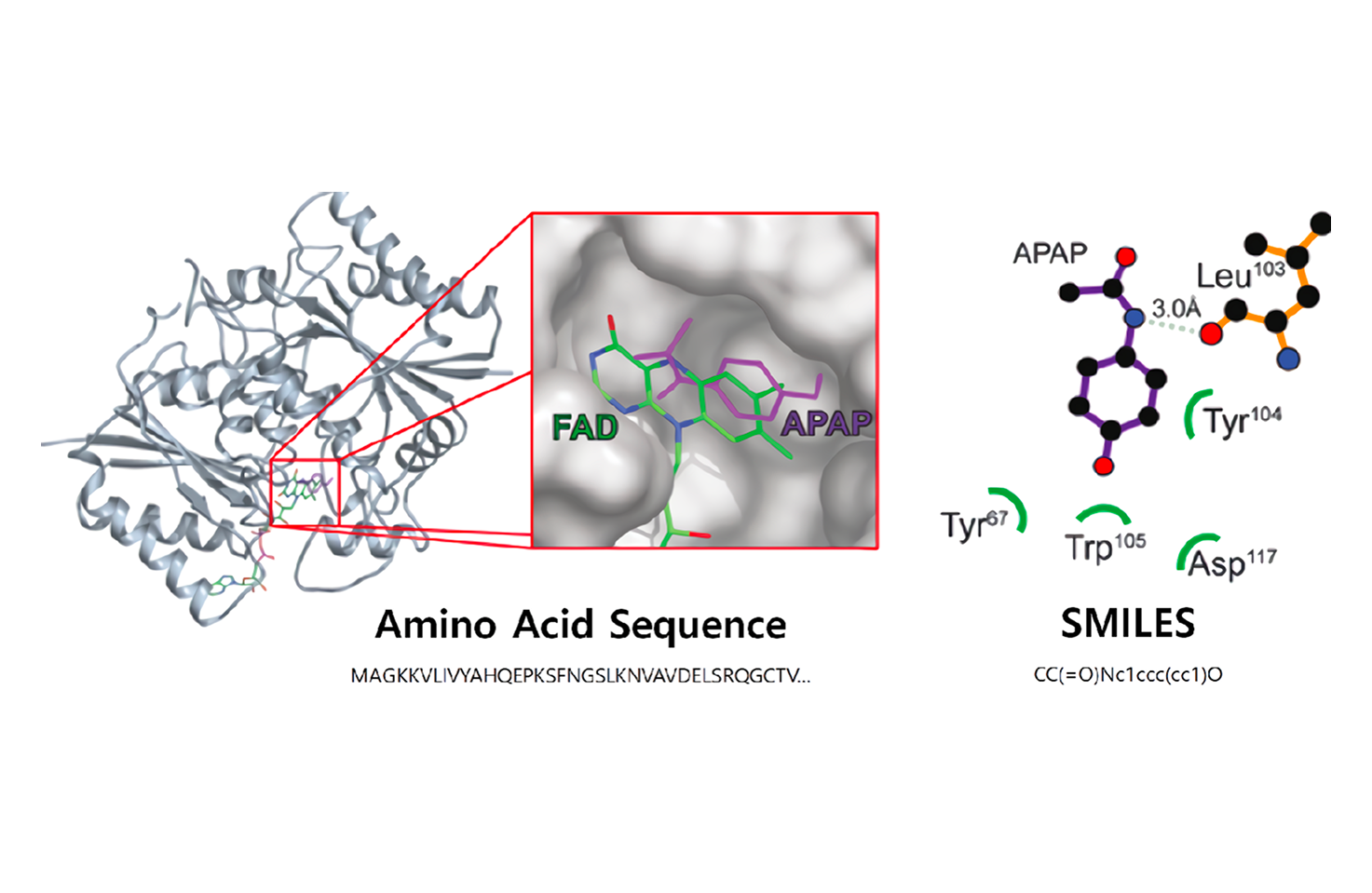
LiLac-Biomarker
Before drug target interaction experiments, candidate compounds are selected through drug screening to enable rapid drug discovery. Successful prediction of drug-target interactions helps avoid unnecessary development costs and improves processes by helping make critical decisions.
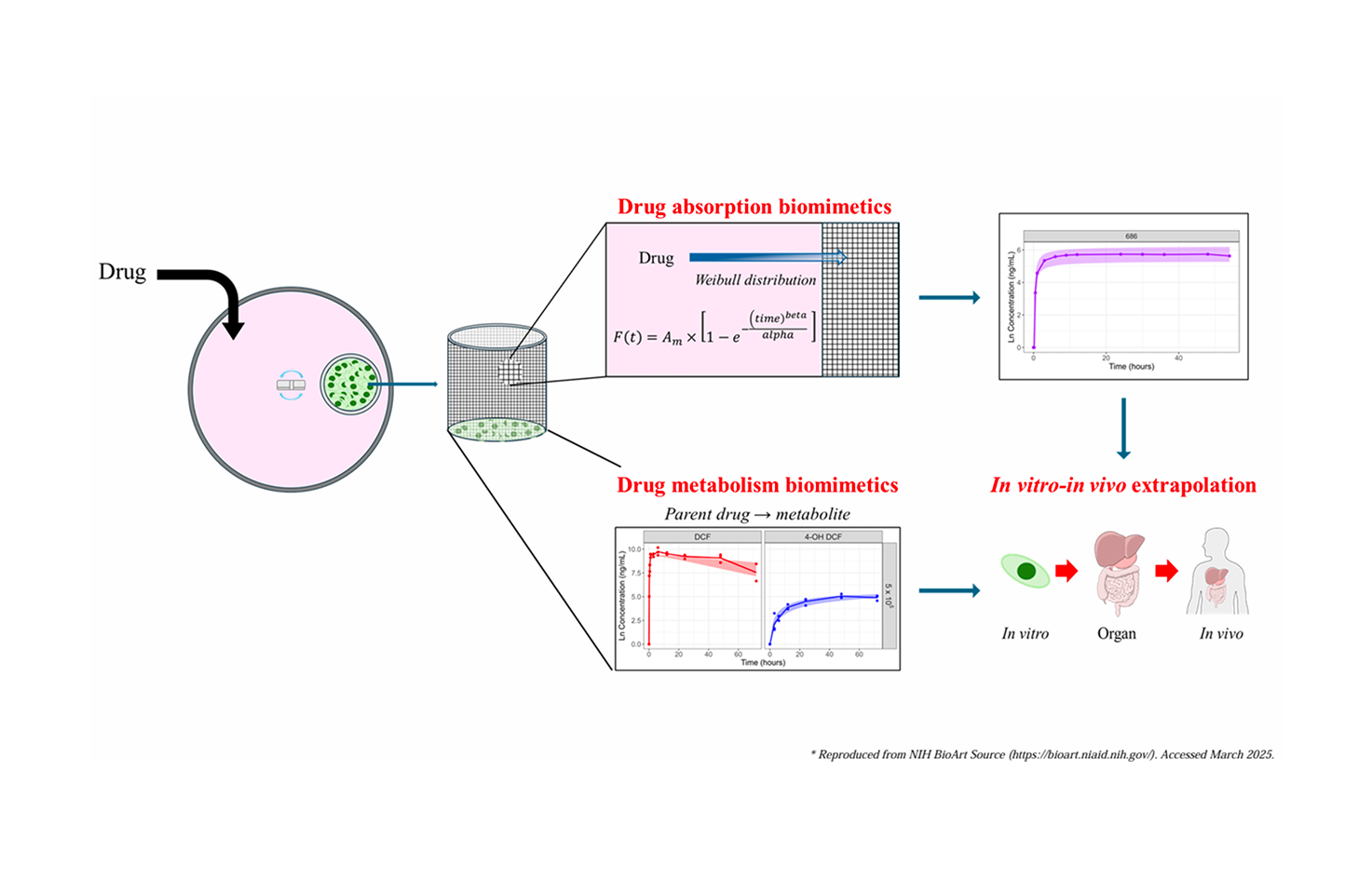
PK simulation platform for biomimetic in vitro system
This platform is an interactive R Shiny-based web application designed to predict in vivo drug kinetics by integrating a patented biomimetic in vitro system (Korean Patent No. 10-2022-0153547) with mechanistic pharmacokinetic modeling. Leveraging experimental data on drug diffusion and cellular metabolism from the porous mesh-based system , the platform simulates the complex processes of drug absorption and metabolic clearance. This model-based strategy aims to provide a reliable, animal-free tool for pharmacokinetic prediction, thereby supporting the 3R (replacement, reduction, and refinement) principle by reducing the reliance on animal testing in drug development.
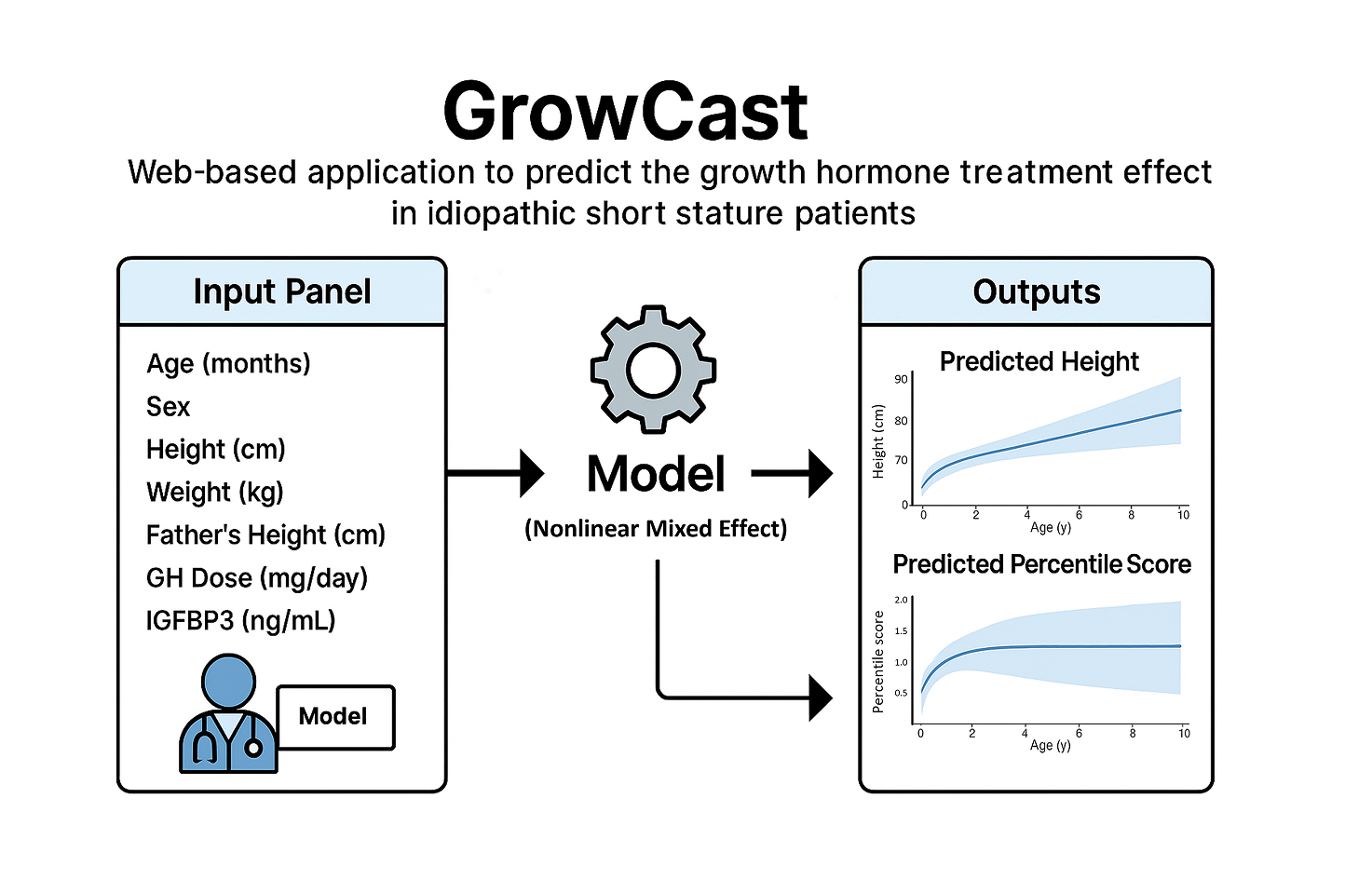
GrowCast
GH Effect Predictor for Idiopathic Short Stature Patients
GrowCast is a web-based R-Shiny application that predicts the growth hormone (GH) treatment effect in patients with idiopathic short stature (ISS). By entering patient information and treatment parameters, the app provides visual forecasts of expected height trajectories and percentile changes. The model applies a Nonlinear Mixed Effect model to deliver interpretable and accurate predictions. The output displays predicted height curves (with uncertainty intervals) and percentile scores in interactive graphs. With its intuitive UI and instantly reactive interface, users can easily assess the expected treatment outcomes.
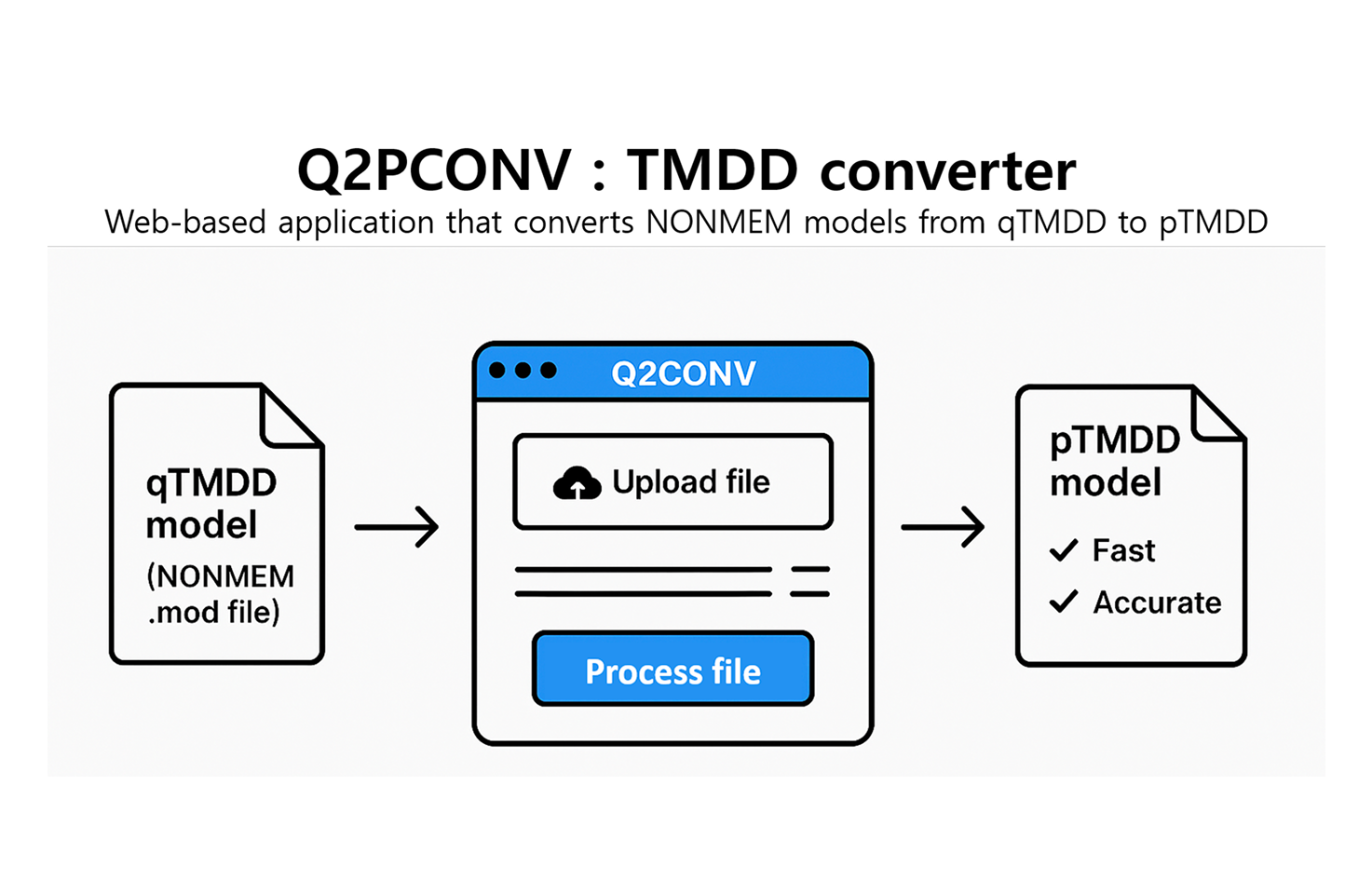
Q2PCONV (Convert TMDD)
Q2PCONV is a web-based R Shiny tool that converts qTMDD models into the newly developed pTMDD approximation. The pTMDD model, derived from the qTMDD model via first-order Taylor expansion, provides higher accuracy than traditional Michaelis-Menten models while being faster to compute than the Quasi-Steady-State (qTMDD) approach. Users can upload NONMEM .mod files and specify options such as receptor type, observation type, and receptor compartment. With a single click, the tool processes and translates the qTMDD model into pTMDD format. The converted file can then be reviewed and downloaded directly from the application.
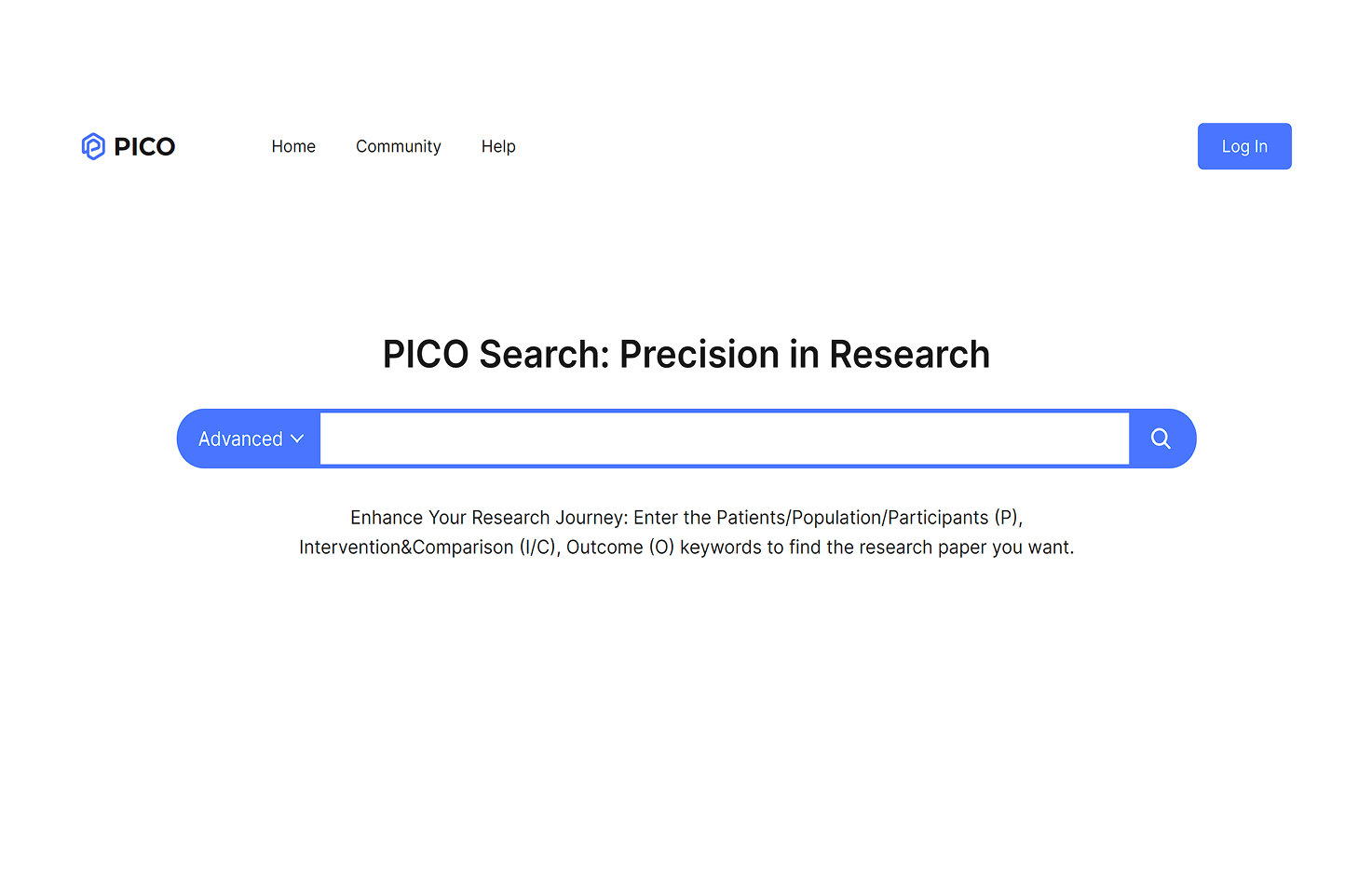
AI-PICO
The AI-based PICO (Patients/Population, Intervention/Comparison, Outcome) framework helps researchers efficiently conduct systematic literature reviews by enabling rapid identification of relevant studies using P, I/C, and O keywords.
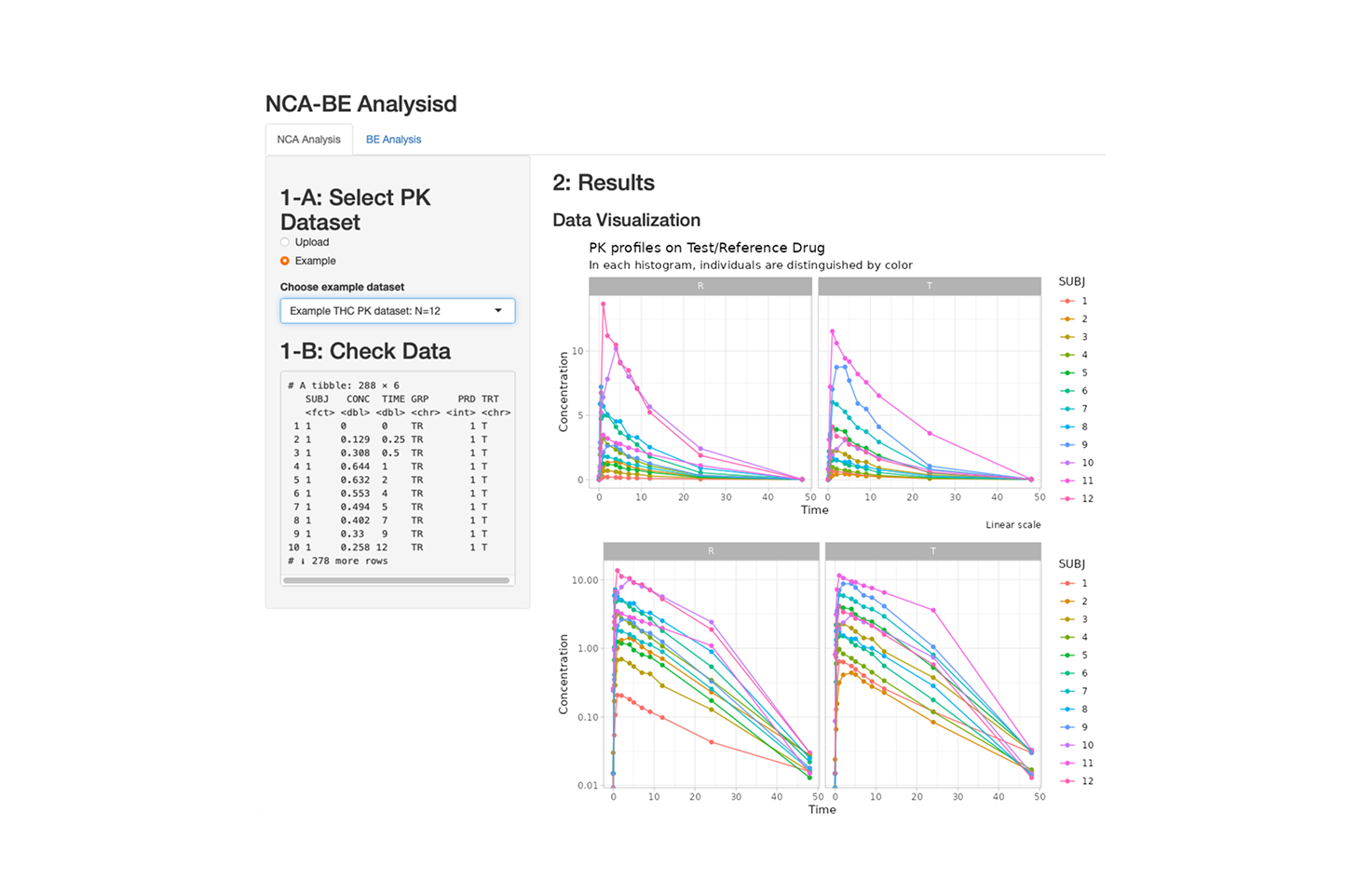
Perform Basic NCA and Bioequivalence Test for Investigated Drug
A tool to perform basic non-compartmental pharmacokinetic (NCA) analysis and conduct standard bioequivalence testing between an investigated drug (Test) and its reference formulation (Control). Users can quickly explore exposure parameters and evaluate BE criteria through an intuitive interface.
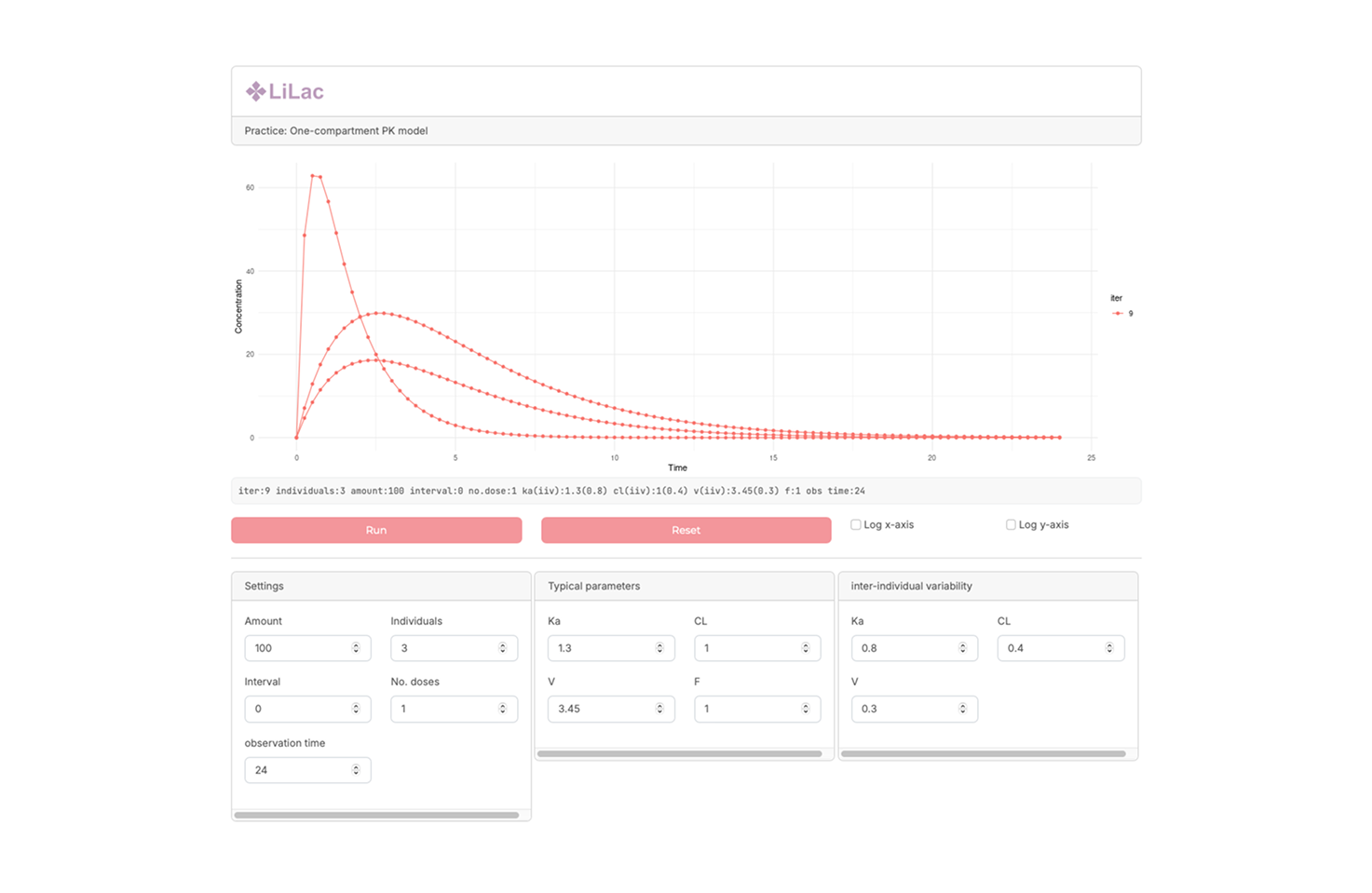
Basic PK simulator (Lilac) PK Profile generation with Various dosing condition
A simple pharmacokinetic simulator designed to generate drug concentration–time profiles under various dosing conditions. This application allows users to compare scenarios such as single vs. multiple dosing, altered intervals, and dose adjustments, making it useful for both education and exploratory PK analysis.
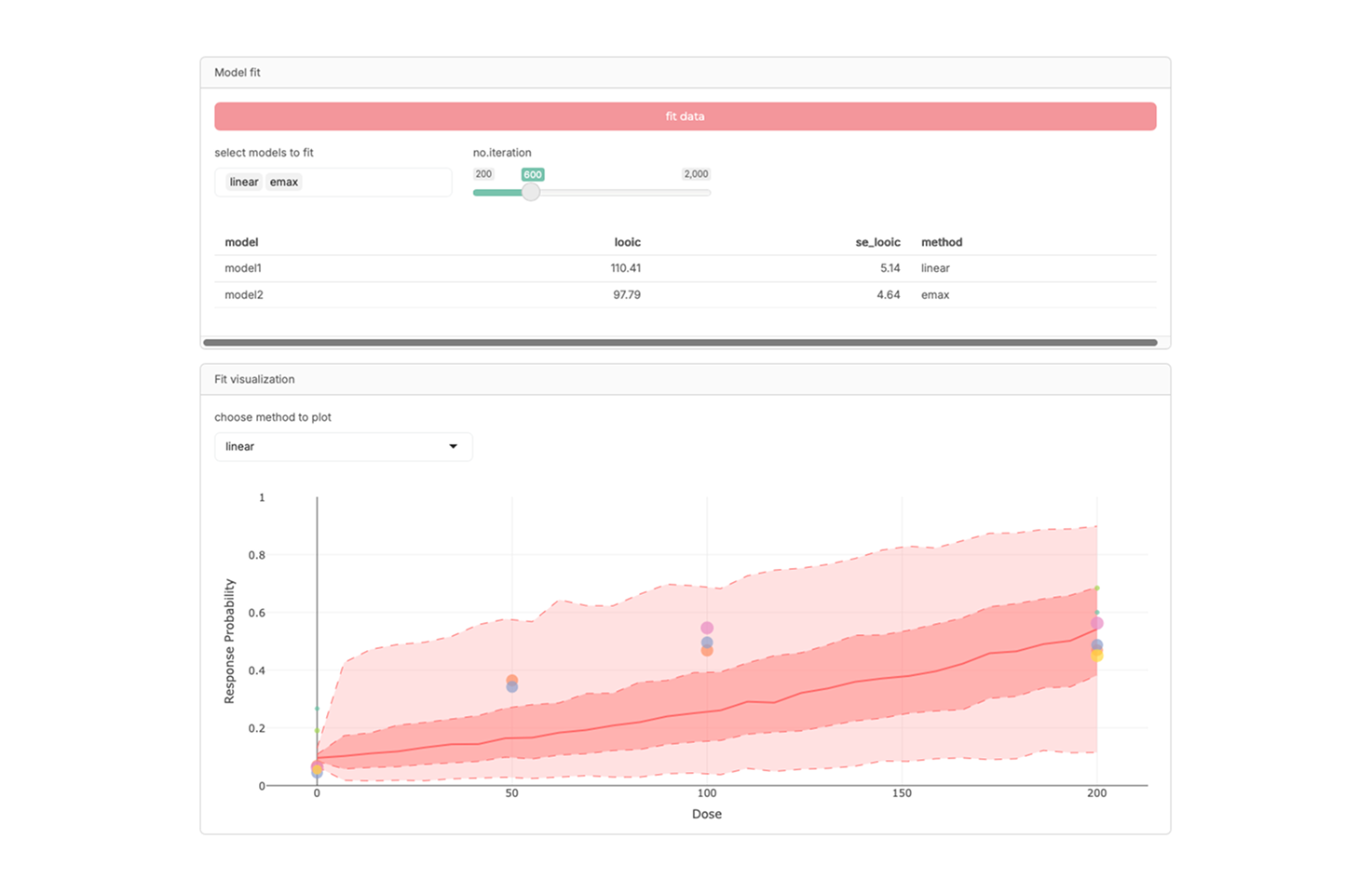
R-shiny model-based meta-analysis for dose-response relationship exploration
An interactive R-Shiny application for conducting model-based meta-analysis (MBMA), particularly focused on exploring dose–response relationships across studies. It supports visualization, integration of heterogeneous data, and quantitative assessment of drug effects, providing a practical platform for dose optimization research.
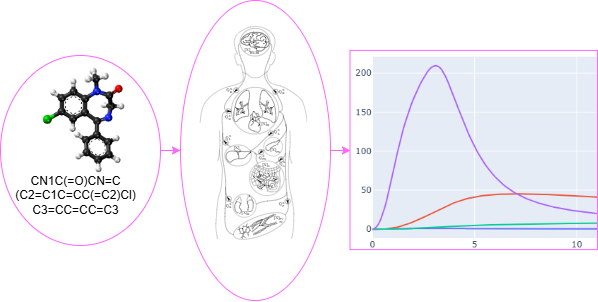
AI-PBPK
ADMET & Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Simulation
This tool predicts the Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, and Toxicity (ADMET) properties of a chemical compound from its SMILES string. These predicted parameters are then used to run a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) simulation, providing insights into the compound's behavior in the body.